When and Why to Wear a Mask or Respirator
What is the difference between a mask or respirator?
Both masks and respirators can support your efforts to stay healthy. Which is best for your situation? Read more to learn about the types of protection available.
Masks
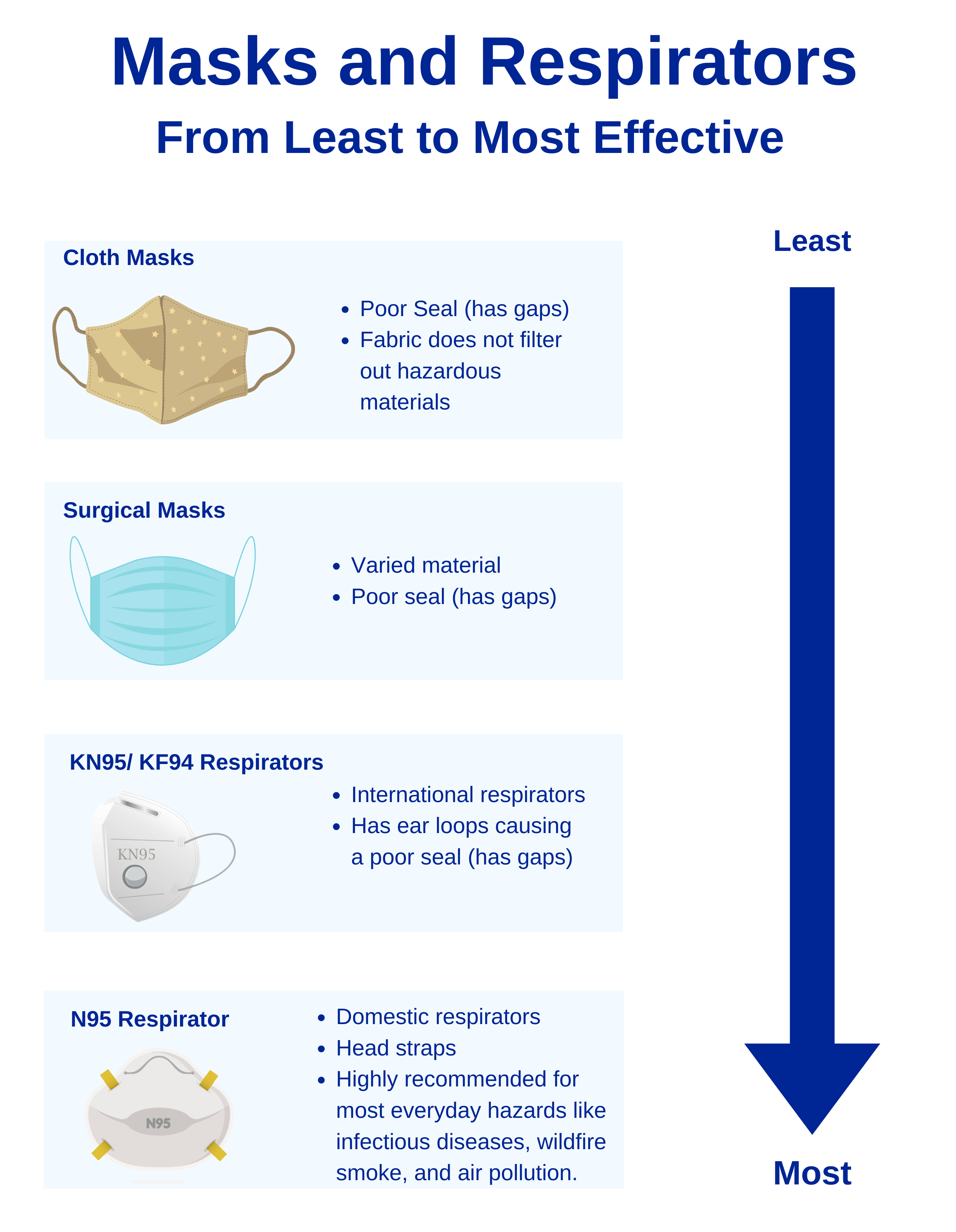
Masks are loose-fitting coverings for your nose and mouth. They attach using ear loops and have gaps around your face. Particles can travel through these gaps and enter your nose or mouth. When you wear a mask, you can protect others because they are less likely to breathe in your germs. Masks offer the least protection to the wearer. Examples of masks are surgical and cloth masks.
|
|
Respirators
Respirators are coverings for the nose and mouth that fit more tightly around the face. They attach using ear loops or head straps. Respirators offer much more protection than masks. They filter particles like smoke, mold, dust and germs from the air you breathe. It can also limit the spread of germs to those around you when you are sick. Examples of respirators are N95, KF94 and KN95 respirators.
|

|
When to Wear a Mask or Respirator
Protection Against Respiratory Viruses
Examples of respiratory virus infections are
COVID-19,
influenza, and
respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
If you test positive for a respiratory virus,
masking is recommended. See
Preventing Spread of Respiratory Viruses When You're Sick for more details.
If you think you were exposed and will be around someone who is high risk, consider wearing a respirator.
If you are at
high-risk of becoming severely ill, consider wearing a respirator. For example, when you are in an indoor public setting with poor ventilation. Or when you are traveling on public transportation.
People who are at high risk for severe respiratory infections include:
- Older adults, especially those 65 and older
- People with certain chronic or medical conditions such as a heart disease or cancer
- People with weakened immune systems
- People who are pregnant or were recently pregnant
- People with disabilities
- People who are in a skilled nursing facility and other long term care facilities
- Children younger than 5 years, especially infants younger than 6 months
Protection Against Harmful Environmental Exposures
Wildfire Smoke
When it’s smoky outside, the best way to prevent smoke inhalation is to stay indoors. For people who must go outside in areas with smoke or ash, they should wear a respirator, such as an N95. Respirators are capable of filtering the harmful particles that can cause breathing problems.
Mold
Mold is part of the outdoor environment. It becomes a problem when it grows indoors because water or moisture are present. Mold can link to
health conditions such as asthma and respiratory infections. Mold in homes can come from a plumbing leak or poor air ventilation. It can also come from heavy rain and flooding. These events can cause water damage in homes and allow mold to grow. If you are unsure if mold is in your home, visit the
CDPH Mold page to learn more. Wear a N95 respirator to protect yourself from breathing in mold after a flooding event. Learn more at
CDC What You Can Do to Protect Your Respiratory Health During Disaster Clean up.
Valley Fever
In certain areas of California, the fungus that causes Valley fever grows in the soil and may be in outdoor dust. When working or spending time outdoors in these dusty areas, wear a N95 respirator. Use a respirator to protect you from breathing in dust and fungal spores that can cause Valley fever. Learn more at
Valley Fever Prevention and at Valley Fever Safety in the Workplace.
Choosing the Right Mask or Respirator
N95 Respirators
N95 respirators provide the most
protection. They can filter 95% or more of particles in the air. They are also tight-fitting. An N95 respirator cannot protect against gases and vapors. Gases and vapors come from activities such as painting or cleaning with bleach. Learn
how to use N95 respirators (PDF).
Adults should use an approved N95 respirator. These are approved by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). N95s have two head straps to secure a snug fit around the face. Authentic N95 respirators have specific markings. Learn more about
counterfeit (fake) respirators.
|
KN95 and KF94 Respirators
KN95s and KF94s are respirators that meet international standards. They provide less protection than N95s because they have ear loops. Respirators with ear loops provide a less-snug fit than respirators with head straps. These respirators are not approved by NIOSH. They cannot be used in the workplace where respirators are required.
|
|
|
Fitting your Respirator
Masks and respirators filter out particles from the air. Masks cover your nose and mouth but are loose fitting. The goal is to cover your nose and mouth without any gaps. Check for any gaps by cupping your hands around the outside edges of the respirator.
A respirator should fit comfortably on the bridge of nose. Refer to
How to use an N95 Respirator for further guidance. If it does not fit properly, the respirator will not provide the best level of protection. Any facial hair may prevent it from fitting snugly to your face. If possible, maintain a clean shave. See
facial hair examples (PDF, 5.1 MB).

Surgical Masks
Surgical masks include various types of loose-fitting disposable masks. These masks can block large droplets but don’t fit close to the face. Even when worn tightly, surgical masks provide much less protection than a respirator.
|
Cloth Masks
Cloth masks are less protective than surgical masks or high-quality respirators.
|
|

|

|
How to Care for your Mask or Respirator
Before using a mask or respirator, check if there is an expiration date printed on the packaging. If it is expired, throw them away.
You should also throw away disposable masks once they become damaged, wet, or dirty. Used cloth masks should be washed as soon as they become wet or dirty. Clean and dry masks can be stored in a breathable bag.
Respirators are not reusable. Throw them away if they become damaged, wet, or dirty. Do not wash your respirator or put it in the oven or microwave to try to sterilize it. If the respirator feels loose on your face and the straps are stretched out, then replace it.
For Children
Masks can be worn safely by children 2 years of age and older. There are rare exceptions. Children under age 2 should not wear a mask. Choose a mask for your child that has the best protection, best fit, and one your child will wear.
Masks should fit over the nose and under the chin with no gaps around the edges. They should not prevent your child from seeing.
KF94s and KN95s are available in “child” or “extra-small” sizes. N95 respirators might come in smaller sizes that fit older children. They may not have been tested for broad use in children.
Who Should
NOT Wear a Mask
Masks are not recommended for:
- Children under 2 years of age
- People with breathing, lung or heart issues
- People who are unconscious or unable to remove the mask without help
Wearing a mask or respirator can be hard for some people
Wearing a mask may be difficult for people with sensory, cognitive, or behavioral conditions. They may also be difficult for people who are hard of hearing or people who communicate with a person who is hard of hearing because seeing the mouth may be needed to communicate.
Respirators and heat illness
Respirators can increase the risk of heat illness. This can happen if it is hot or if you are physically active. To prevent this:
- Take breaks often.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Use a respirator with an exhalation valve. It can help you breathe easier when it is hot or when you are active. Keep in mind, a respirator with an exhalation valve may not protect others. If you are sick, the air you breathe out can escape through the valve.
Consider removing the respirator or moving to a place with cleaner or cooler air if:
- You have difficulty breathing
- Are getting dizzy
- Have other symptoms
If you have concerns about wearing a mask, talk to your health care provider before using one.
Other Considerations
This information is for a general audience. Some
workplaces (PDF), local health departments, and
Cal/OSHA may have different requirements.